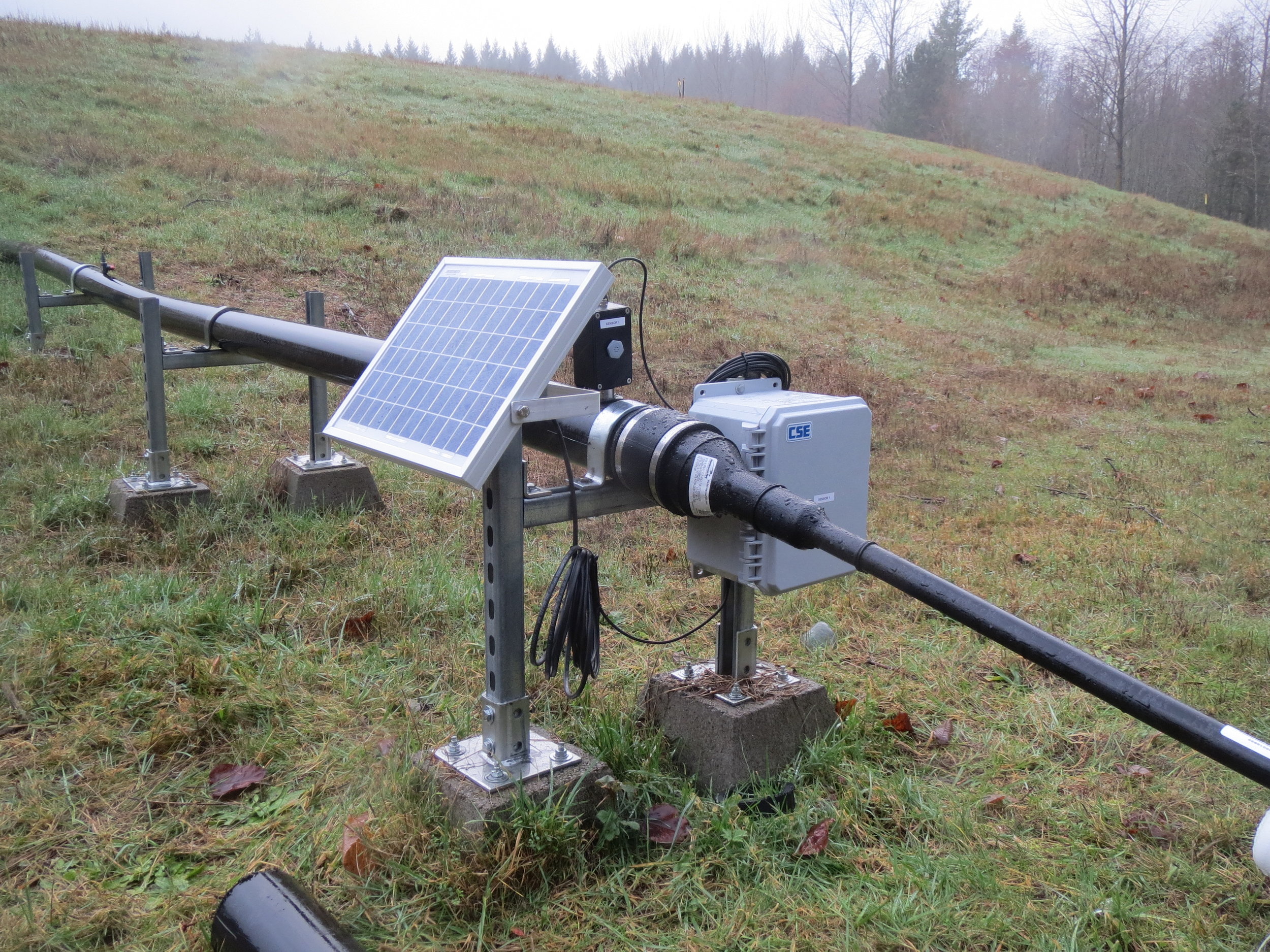
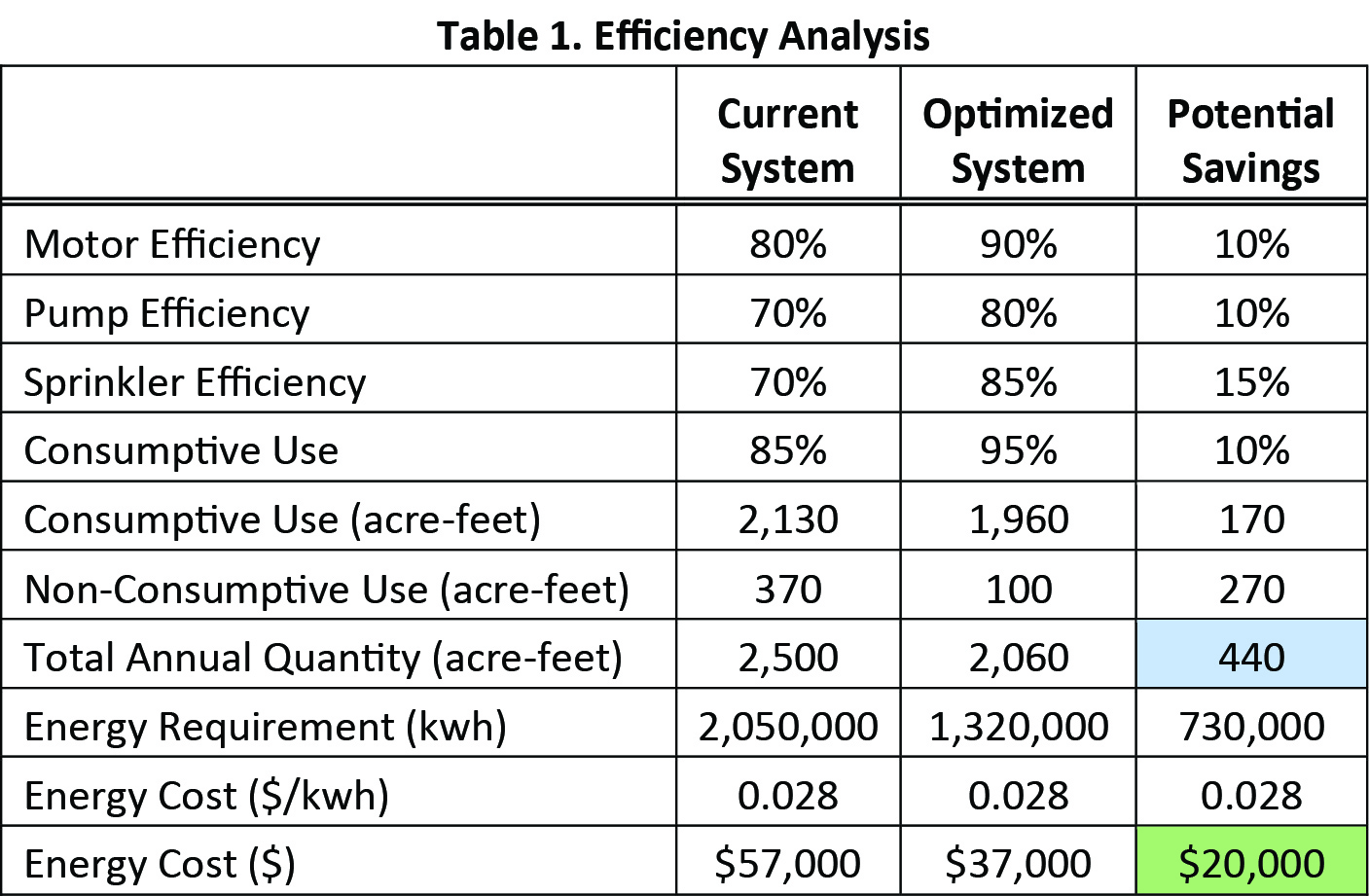
Scientists from the CSE Corporation (a company developing cutting-edge gas detection devices used in air-quality monitoring) and Aspect remediation engineers are working in partnership to develop new methods for continuous methane-gas monitoring at landfills. CSE’s methane-gas monitoring products use solar-powered instruments outfitted with telemetry. Solar power eliminates the need for frequent battery replacement while telemetry allows remote monitoring of the data. With cooperation from King County Solid Waste Division, CSE has provided Aspect with test units to install at several of the County’s closed landfills to gauge the effectiveness of this technology for the landfill industry.
CSE has roots in the mining industry and a history of innovations, including the first self-contained rescue-breathing apparatus for use by mine personnel. KCSWD, Aspect, and CSE are testing the devices ability to monitor methane, a primary source of greenhouse gas emissions from landfills.
Got methane? CSE remote methane monitoring setup with telemetry and solar panel on a passive landfill gas collection system in King County, Washington.